FUT treatment
Follicular Unit Transplantation is a method in which a strip of the scalp is taken from the donor area - generally the back of the head. It then involves extracting from this strip individual hair follicles / follicular units under the microscope and preparing them for implantation. These Follicular Units, or FUs for short, grow in groups of 1 - 4 or sometimes even 5 follicles. The transplant material thus obtained is then implanted into a prepared recipient area. Hairs extracted this way retain their genetic information, growing again naturally in the recipient area after transplantation. To obtain the requisite number of hair follicles needed for the transplant to look natural, the patient's existing hair density in the donor area is determined as exactly as possible (density measurement). This is done by counting the number of FUs per square cm before FUT treatment and is the basis for determining the size of the strip of scalp to be removed. The strip of scalp (or any other area covered in hair) is then removed using a scalpel. This is done under local anaesthesia, meaning that no pain at all is felt.
FUT - a modern successful method
FUT involves four main activities:
- extracting the donor material
- preparing the individual hair units / hair follicles
- preparing the implantation area
- implanting the donor hairs


Over the past decade major progress has been made in all four activities, meaning that graft survival rates have improved greatly and results become increasingly natural-looking. The focus remains on the two most important objectives of any hair transplantation: fulfilling patient wishes with regard to optimal naturalness and achieving optimal hair density. Current FUT techniques achieve these objectives - even though the transplantation of the fine grafts is a very complex and demanding procedure requiring an experienced and careful hair surgeon.
The history of FUT

The first successful hair transplants were already being performed in the first half of the last century, with the transplanted hair groups not just rooting on the bald patches but also for the most part producing strong hairs. The various hair transplantation methods now in use developed over time. Over the years it was discovered that hair grows in natural groups, the so-called follicular units. This discovery led to the introduction of Follicular Unit Transplantation, or FUT for short.

The FUT-technique involves removing a strip of the scalp from the donor area, in most cases the back of the head. From this strip, individual follicular units i.e. hair root groups are extracted under a microscope. In doing so, attention is paid to maintaining the way they are arranged as a group. These extracted units are then inserted into micro-incisions in the implantation area and arranged in such a way that as far as possible a natural pattern with natural hair distribution is created.
FUT quickly replaced mini-/micro-graft transplantation, becoming the method of choice for implanting donor hairs into larger-sized scalp areas all in one go. For many years now, follicular unit transplantation has been the most commonly used method for transplanting hair.
Which patients are suited for FUT?
The biggest advantage associated with a strip extraction is the large number of FUs that can be made available during a single transplantation session. In contrast to Follicular Unit Extraction, many more hairs can be extracted within a much shorter period of time, thereby reducing effort. The FUT method is primarily suited to patients classified as Norwood III - VII, as these need many more hairs to be transplanted. Patients older than 30 - 35 are also deemed as being more suited, as the occurrence of the so-called stretch-back effect is less pronounced. FUT is also suitable for combined transplantations, for instance when scarring from a previous hair transplant needs to be corrected or at least decreased and when at the same time a hair transplant is to be performed.
The limitations of FUT
Type of scar and its development
The scar left by FUT at the back of a patient's head is very narrow, in most cases just 1 - 2 mm wide. The length differs. It is always a linear scar, and more or less visible. Its visibility is not just dependent on the hair surgeon's skill and experience and the technique he uses, but also on such individual factors as the patient's age, the type of skin, skin characteristics, skin tension and the healing process. How the scar develops is not foreseeable, even when past wounds have healed nicely. Also needing to be taken into account is the fact that a linear scar can change through the healing process and the tension of the scalp (the so-called stretch-back effect). This can occur directly after the transplantation or in the course of the six following months. The wound is sutured or stapled, meaning that there are stitches or staples needing to be removed. Dependent on the size of the FUT scar, hair can often not be worn shorter than 10 - 15 mm without the scar being seen.
The operation, healing process and possible post-operation complications
Ideally, the donor area should be shaved before the operation, in particular when a high density-FUT or mega-session is involved. Exceptions can be made and should be personally discussed with Dr. Feriduni. Where only small transplants are involved, in certain cases no shaving is needed at all. Though very seldom, complications can occur during or after the transplantation, as is the case with any operation. These include scar pain and wound infections. In the donor area a feeling of numbness can occur, or tension can be felt. Moreover the healing process can last quite a long time (up to 2 weeks) due to the size of the incision. After transplantation patients should desist from active sport (bodybuilding, martial sports) for a period of about 6 weeks. Light sport activity such as jogging, swimming, cycling can be started after about 2 weeks, though care needs to be taken. When extracting the donor hairs, hair follicles situated in the immediate vicinity of the cut may be damaged or injured. With the wound being sutured or stapled, this is another possible cause of damage to hair follicles. After the operation, swelling can take place. In some cases transplanted FUs may fall out.
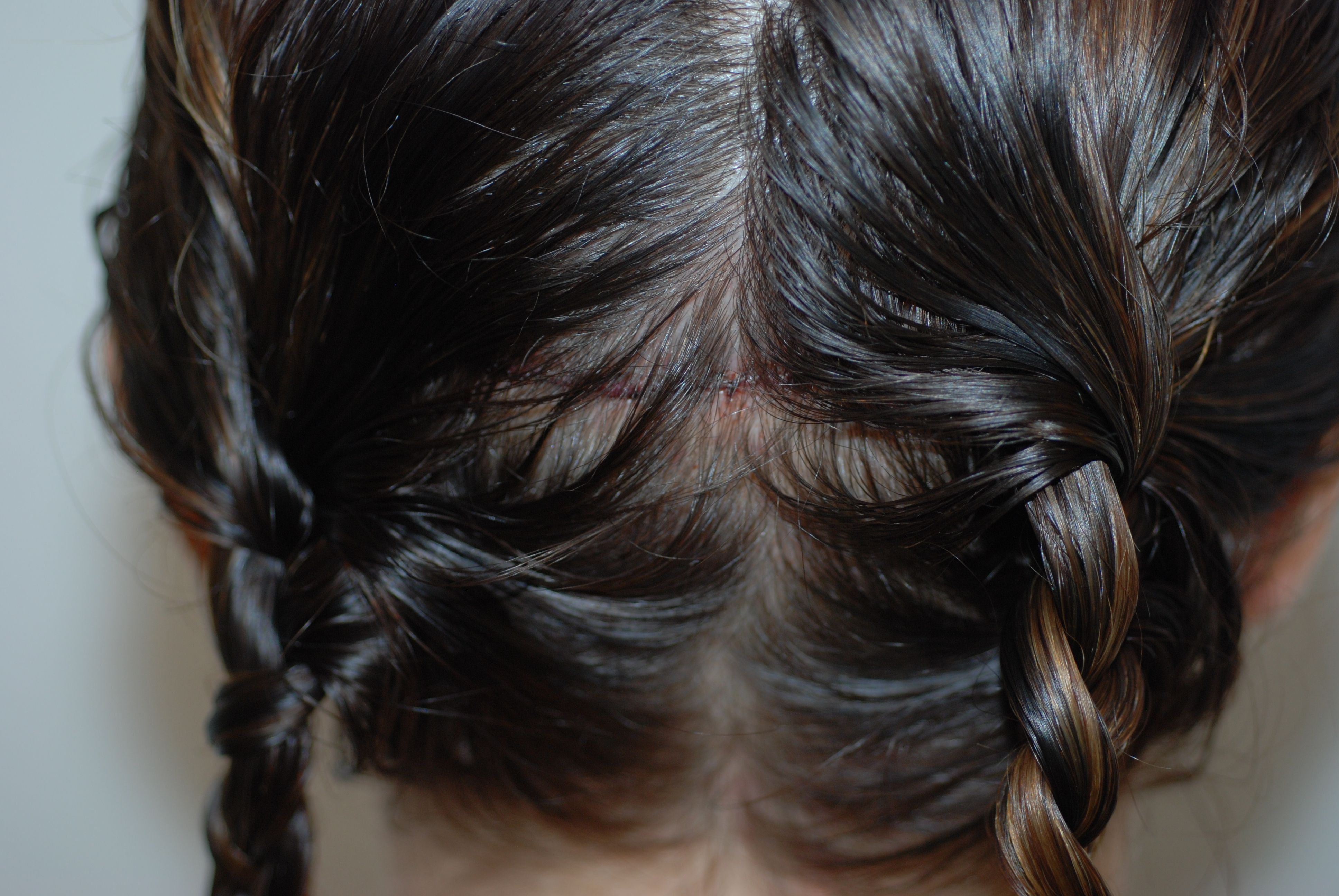

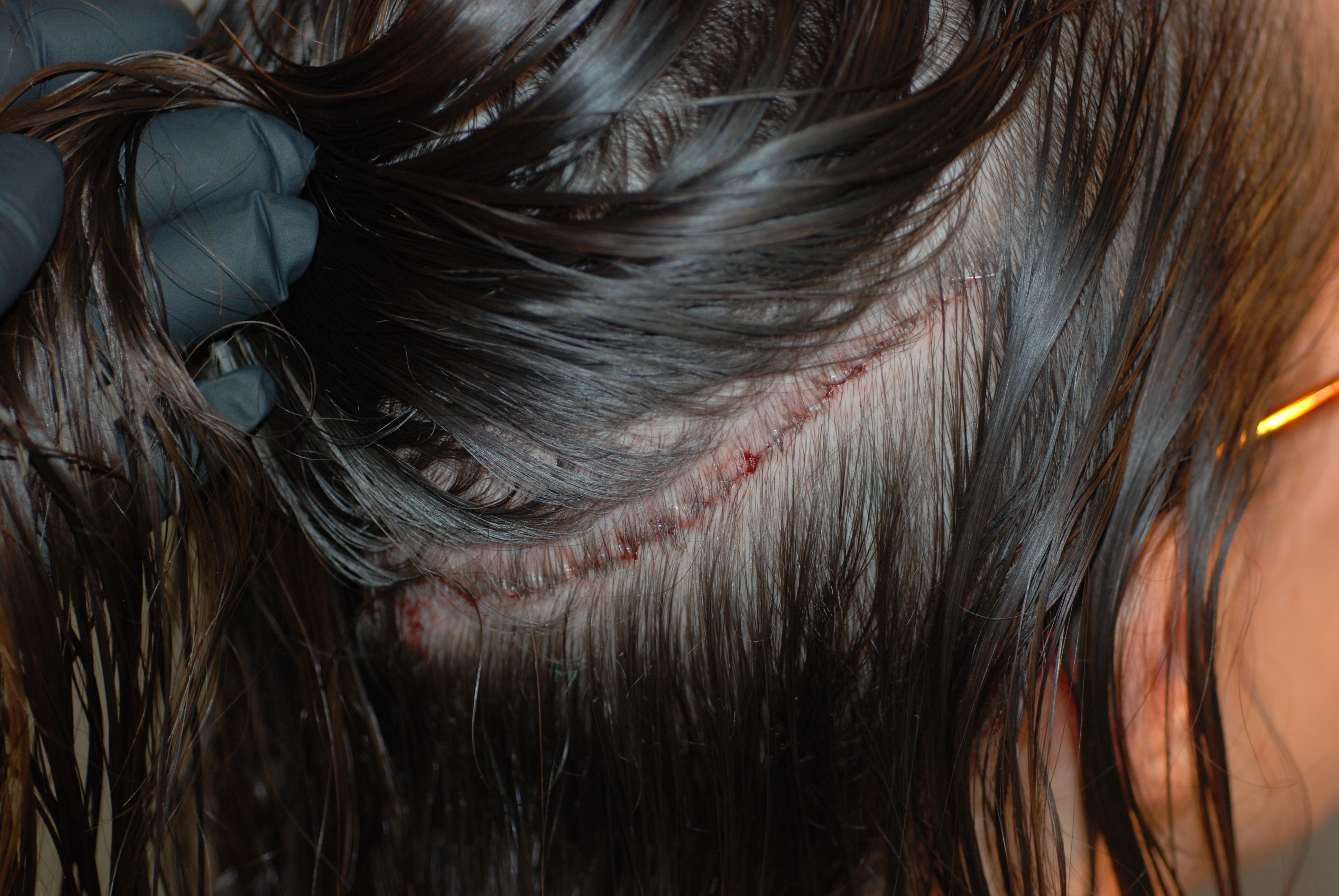
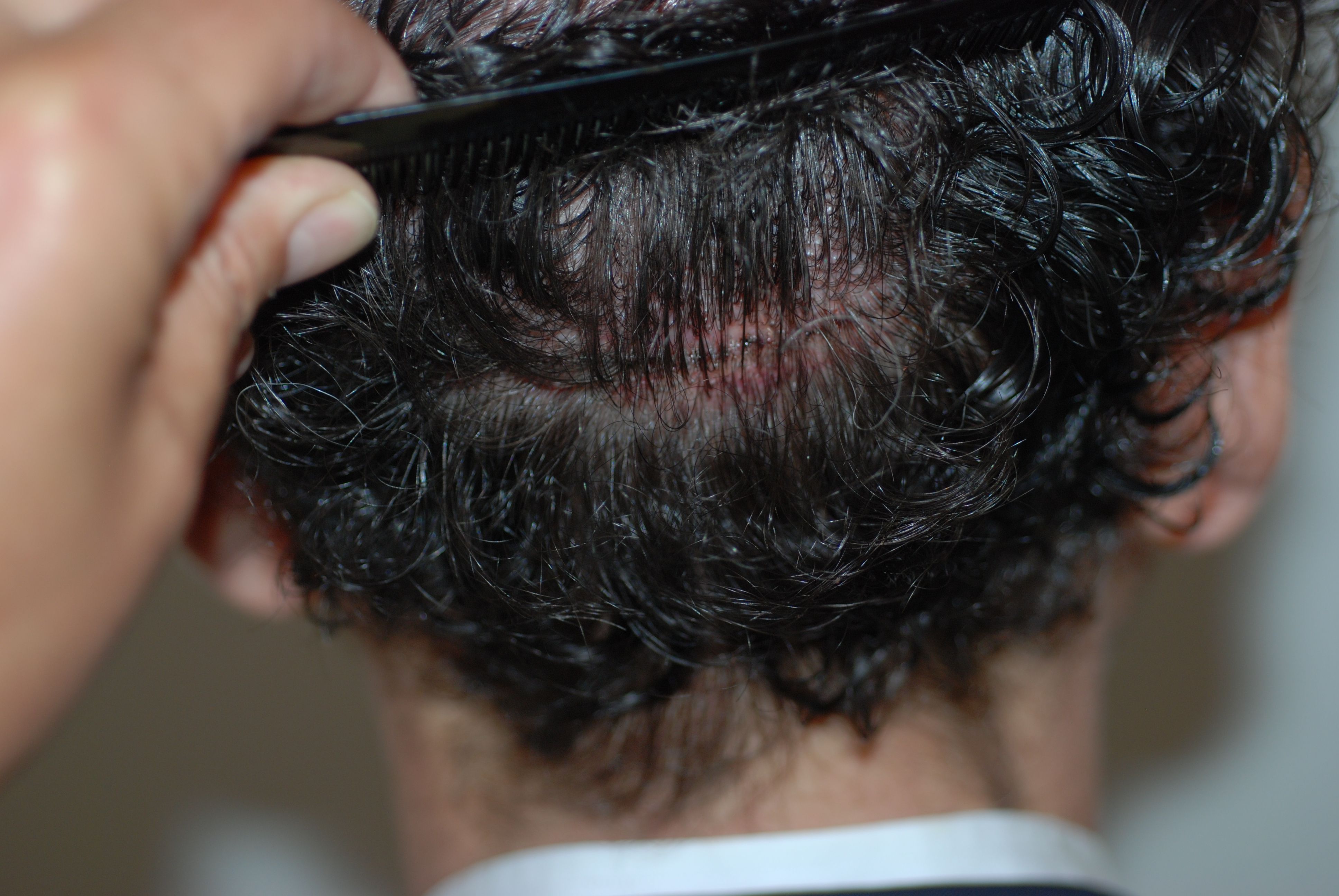
Trichophytic Closure
This is a technique used to make the scars caused by the removal of the strip of skin practically invisible. Further advantages over previously used methods are that the scar becomes a lot finer and that the method can be used in all commonly used transplantation methods. Trichophytic closure (or tricho for short) involves overlapping the edges of the wound when suturing or stapling them. One side of the existing skin is cut at an oblique angle, after which the adjacent skin flaps are brought together to close the wound. Due to the angle of the cut, they overlap. One piece of scalp tissue now lies underneath another one - and in it also hair follicles, which then slowly grow through the tissue (i.e. through the ensuing scar), thereby concealing the scar and making the donor area look natural. When this closure method has been used after an FUT, it becomes quite possible for patients to wear their hair short - i.e. 6 - 8 mm long. This means that this technique is an alternative to Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) for patients wanting to wear their hair short. Trichophytic closure can also be used on patients already having had an FUT to improve the donor scar. This technique is also used on an initial FUT operation and is very suited for reconstructive or corrective treatment.
The success of trichophytic closure is not just dependent on the ability and experience of the hair surgeon, but also on the healing process and the characteristics of the patient's skin. Not every patient is suitable for Tricho-Closing. This applies especially to younger patients and it is therefore up to Dr. Feriduni to decide which closure technique to use.
Practical information on your FUT treatment by Dr. Feriduni
Fill in the free online consultation form
Contact us for more info
+32 11 299 790 or This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.